Have you ever wondered how big a horse’s brain is and how it compares to other mammals? The size of a horse’s brain is a fascinating topic that sheds light on the cognitive abilities and behavior of these majestic animals. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the size and characteristics of a horse’s brain, providing valuable insights into its structure, functions, and significance within the equine world.
Anatomy of a Horse’s Brain
The horse’s brain, a crucial component of the nervous system, is responsible for processing information, coordinating bodily functions, and regulating behavior. The equine brain shares many similarities with the human brain in terms of overall structure and organization. However, there are also notable differences that reflect the unique adaptations and instincts of horses.
Size of a Horse’s Brain
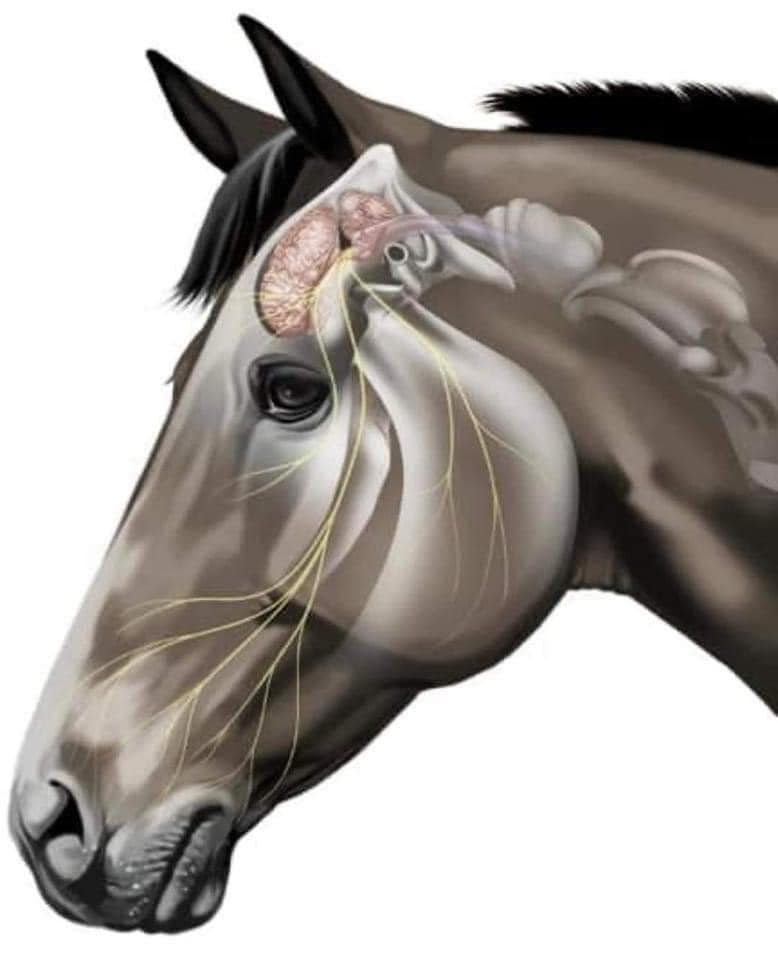
On average, a horse’s brain weighs approximately 22 ounces (1.4 pounds) or about 0.06% of its body weight. The size of a horse’s brain can vary slightly depending on the breed and individual. In comparison to the human brain, which weighs about three pounds on average, the horse’s brain is smaller in size. It is important to note that brain size alone does not directly correlate with intelligence or cognitive capabilities. The equine brain is highly specialized to meet the specific needs and behaviors of horses.
Cognitive Abilities and Intelligence
While the horse’s brain may be smaller than the human brain, it possesses remarkable cognitive abilities. Horses exhibit complex learning, memory, and problem-solving skills. They have the capacity to recognize and respond to familiar individuals, learn new tasks, and exhibit social intelligence within their herd. The intelligence of a horse is not solely determined by brain size but is shaped by their experiences, environment, and innate instincts.
Brain-Related Behaviors and Responses
The horse’s brain plays a crucial role in governing their behavior and responses to stimuli. Instinctual behaviors, such as flight or herd dynamics, are regulated by the brain’s complex neural networks. The horse’s brain enables them to perceive and interpret sensory information, facilitating their ability to react to their surroundings. The brain’s influence on behavior and responses is evident in various aspects of equine life, including communication, movement, and interaction with humans and other horses.
Communication and Social Interactions
The horse’s brain also contributes to their communication skills and social interactions. Horses possess the ability to understand and respond to subtle cues from both humans and other horses. They can interpret body language, vocalizations, and facial expressions, forming bonds and hierarchies within their herd. The equine brain’s processing capabilities enable horses to communicate their needs, establish social connections, and navigate their environment.
Brain Health and Well-being
Maintaining brain health is crucial for the overall well-being of horses. A healthy and well-functioning brain ensures optimal cognitive function, emotional well-being, and physical coordination. Factors such as proper nutrition, regular exercise, and a stimulating environment contribute to brain health in horses. Monitoring for signs of neurological issues or abnormalities, such as changes in behavior, coordination difficulties, or cognitive decline, is essential for early detection and appropriate intervention.
Brain Research and Advancements
Advancements in neuroscience and brain research have shed new light on the intricacies of the equine brain. Advanced imaging techniques and studies focusing on brain functions have expanded our understanding of how horses perceive, process, and interact with their environment. These advancements have significant implications for equine health, training techniques, and overall welfare.
Is a horse brain the size of a walnut?
No, a horse’s brain is not the size of a walnut. While it is true that a horse’s brain is smaller compared to the human brain, it is significantly larger than a walnut. The size of a horse’s brain can vary slightly depending on the breed and individual, but on average, it weighs about 22 ounces (1.4 pounds). The horse’s brain has a complex structure and plays a vital role in their cognitive abilities, behavior, and overall functioning.
What is the average size of a horse’s brain?
The average size of a horse’s brain is approximately 22 ounces (1.4 pounds), although there can be slight variations depending on the breed and individual. The size of a horse’s brain is generally smaller compared to the human brain, which weighs about three pounds on average. It is important to note that brain size alone does not determine intelligence or cognitive capabilities. The equine brain, despite its smaller size, possesses remarkable cognitive abilities and is specialized to meet the specific needs and behaviors of horses.
Do horses have a bigger brain than humans?
No, horses do not have a bigger brain than humans. On average, the human brain weighs about three pounds, while a horse’s brain weighs approximately 22 ounces (1.4 pounds). The size of the brain alone does not directly correlate with intelligence. Humans have a larger brain-to-body size ratio compared to horses, which is believed to be associated with the complex cognitive abilities and advanced problem-solving skills observed in humans. However, it is important to note that horses possess their own unique cognitive capabilities and exhibit remarkable learning, memory, and social intelligence within their species.
What is horse IQ?
The concept of “horse IQ” refers to the cognitive abilities and intelligence of horses. While it is difficult to quantify intelligence in animals accurately, horses exhibit various cognitive skills and problem-solving capabilities. They possess the ability to learn, remember, and apply knowledge in different situations. Horse intelligence is not solely determined by brain size but is shaped by their experiences, environment, and innate instincts. Horses demonstrate adaptive learning, social intelligence, and the ability to form relationships with humans and other horses. However, it is important to recognize that intelligence can vary among individual horses, just as it does among individual humans.
Read: Can Horses Eat Blueberries?
Read: When to Euthanize a Horse with Cushing’s?
Read: What Plants Don’t Like Horse Manure?
Read: Is Horse Meat Halal?
Conclusion
The size of a horse’s brain, although smaller compared to the human brain, plays a vital role in their cognition, behavior, and social interactions. By exploring the anatomy and functions of the equine brain, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable capabilities and adaptations of these magnificent creatures. Understanding the size and significance of a horse’s brain enhances our ability to provide appropriate care, training, and enrichment that support their overall well-being and cognitive development.

